Cheyne-stokes Respirations
Welcome to Medical News Today Healthline Media, Inc. Would like to process and share personal data (e.g., mobile ad id) and data about your use of our site (e.g., content interests) with our third party partners (see a ) using cookies and similar automatic collection tools in order to a) personalize content and/or offers on our site or other sites, b) communicate with you upon request, and/or c) for additional reasons upon notice and, when applicable, with your consent. Healthline Media, Inc. Is based in and operates this site from the United States. Any data you provide will be primarily stored and processed in the United States, pursuant to the laws of the United States, which may provide lesser privacy protections than European Economic Area countries. By clicking “accept” below, you acknowledge and grant your consent for these activities unless and until you withdraw your consent using our. Learn more in our.
It's time you switched to a better browser For a better, secure browsing experience, we've made the tough decision to no longer support early versions of Internet Explorer (8 and below) and Firefox (22 and below). Unfortunately these older web browsers do not support many crucial developments in online security, and therefore represent a threat to your online security, as well as the security of MNT. For the safety and security of your online experience, we strongly recommend that you switch to a more modern browser (we've provided links to a few at the top right of the page). While you will continue to be able to read MNT as normal, your actual experience may not be exactly as we intended and you will not be permitted to log-in to, or register for an MNT account. Thank you, The MNT Team.
Cheyne-Stokes respiration (CSR) is one of several types of unusual breathing with recurrent apneas (dysrhythmias). Reported initially in patients with heart failure or stroke, it was then recognized both in other diseases and as a component of the sleep apnea syndrome. Cheyne-Stokes respiration (CSR) is a form of respiration that is periodic in nature where there is a gradual increase in the depth and rate of breathing, followed by gradually shallower and slower.
Please accept our privacy terms We use cookies and similar technologies to improve your browsing experience, personalize content and offers, show targeted ads, analyze traffic, and better understand you. We may share your information with third-party partners for marketing purposes. To learn more and make choices about data use, visit our.
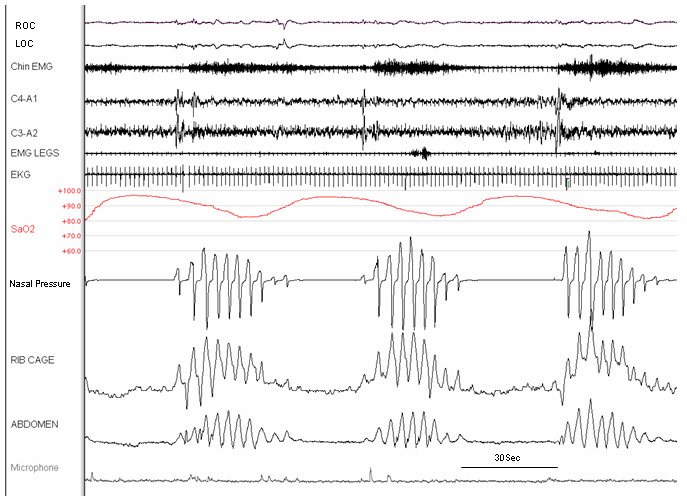
By clicking “Accept and Continue” below, (1) you consent to these activities unless and until you withdraw your consent using our rights request form, and (2) you consent to allow your data to be transferred, processed, and stored in the United States. Cheyne-Stokes respiration, also known as periodic respiration, is an abnormal pattern of breathing. It consists of cycles of breathing, which become increasingly deeper, followed by periods where respiration becomes gradually shallower. There may then be a period of apnea, where breathing briefly ceases, before the cycle begins again. On average, each cycle lasts between 30 seconds and 2 minutes.
This respiratory condition occurs both during sleep and wakefulness, although it is believed to be during sleep. While Cheyne-Stokes respiration usually occurs during slee, it may also happen during waking hours.
People with Cheyne-Stokes respiration usually experience:. Orthopnea: This is shortness of breath when lying down.
Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea: Severe shortness of breath and coughing fits. These usually occur at night, and disrupt sleep. Excessive daytime sleepiness and fatigue: This is caused by periods of interrupted sleep. How does it happen? The physiological processes that lead to the development of Cheyne-Stokes respiration, which involves the cardiovascular, pulmonary, and sympathetic nervous systems, are not fully understood.
However, it is thought to be:. Unstable feedback in the respiratory control system.
Changing levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood cause the cycles of apnea and hyperventilation. Delayed circulation.
Circulation time is increased in people with congestive and Cheyne-Stokes respiration. This is not considered a significant contributor to the cause of the condition, but it is directly related to the length of the abnormal breathing cycles. Another potential cause is reduced blood gas buffering capacity. The bicarbonate buffer system helps maintain the pH of the body by expelling carbon dioxide through exhalation. As those with Cheyne-Stokes respiration hyperventilate, their total carbon dioxide stores are likely to be reduced, which interferes with the carbon dioxide buffering capacity of the body. Low levels of oxygen in the body may also intensify blood gas fluctuations in those with Cheyne-Stokes respiration. Who is at risk of Cheyne-Stokes respiration?
Cheyne-Stokes respiration can occur in people with neurological conditions, or congestive heart failure. Some research estimates that of all people who have moderate to severe congestive heart failure also have significant Cheyne-Stokes respiration. The condition is also recognized as a component of the sleep apnea syndrome. However, many cases of Cheyne-Stokes may remain unrecognized, particularly as it is most common during sleep.
Associated conditions Cheyne-Stokes is usually associated with heart failure or, but it is also linked to several other conditions including. Other abnormal patterns of respiration Kussmaul breathing This condition is also characterized by deep, rapid breathing. However, Kussmaul breathing does not feature the shallow breaths, apnea, or alternations in breathing patterns experienced in Cheyne-Stokes respiration. It remains deep and rapid throughout. Kussmaul respiration can be seen in people with diabetic ketoacidosis or kidney failure. It is a compensatory measure to try and regain a balance between acid and alkaline in the body, as the body tries to rapidly exhale carbon dioxide, which is acidic. Cluster breathing.
Also known as Biot's respirations, cluster breathing is characterized by groups, or clusters, of rapid, shallow breathing. This is followed by periods of apnea. It differs from Cheyne-Stokes respiration in that it does not feature cycles of deep breathing, or gradual alternations in breathing patterns. Hyperventilation Characterized by over-breathing, where breathing is deep and rapid, hyperventilation causes low levels of carbon dioxide and high levels of oxygen in the blood. People who are anxious, stressed, or experiencing a may hyperventilate. Symptoms include dizziness, weakness, fainting, and confusion.

Hypoventilation Breathing that is too slow or too shallow is called hypoventilation. It causes high levels of carbon dioxide and low levels of oxygen in the blood. It may be caused by lung problems, such as. Symptoms include daytime sleepiness, and fainting. Obstructive sleep apnea People with experience momentary periods where breathing stops during sleep. These periods of apnea are caused by upper airway collapse, and may occur each hour. Obstructive sleep apnea is linked to.
Kussmaul Vs Cheyne Stokes
Symptoms include headaches upon waking, difficulty concentrating, and daytime sleepiness. Diagnosis Diagnosing Cheyne-Stokes respiration can be difficult as it most commonly occurs during sleep. Those who are experiencing the symptoms of Cheyne-Stokes or other abnormal breathing patterns should consult a doctor, who may make a diagnosis based on symptoms and a physical examination. If the condition occurs at night, a doctor may recommend a polysomnography, which is a type of sleep study.
This type of study is carried out at a hospital or sleep center. It records heart rate, breathing rate, brain waves, blood oxygen levels, eye movements, and other movements during sleep. Management Management of Cheyne-Stokes respiration may include some or all of the following treatment options. Heart failure treatment Treating the underlying congestive heart failure may help alleviate symptoms of Cheyne-Stokes respiration. CPAP masks are a common method used to treat sleep apnea. Continuous positive airway pressure is the leading treatment for sleep apnea. This therapy uses mild air pressure to keep the airways open.
The individual wears a mask over their mouth, nose, or both. The mask is connected by a tube to a CPAP machine that supplies the tube with a positive flow of air. Observable benefits include better sleep quality, reduced snoring, and less daytime sleepiness. Long-term benefits include control, reduced risk of stroke, and improved memory. However, indicates that CPAP does not increase survival rates in people with heart failure, although other research suggests that of people experience beneficial effects in terms of their Cheyne-Stokes symptoms.
According to the, most insurance companies will cover CPAP treatment. Prevention Preventing Cheyne-Stokes respiration involves preventing the medical conditions that are associated with it, including heart failure and stroke. People with these conditions should ensure they follow their treatment plan to help manage their symptoms, which may help prevent Cheyne-Stokes respiration.
Avoiding exposure to heavy metals and other toxins, which can cause toxic encephalopathy, will also help prevent the condition. Outlook Cheyne-Stokes respiration is a serious condition. As it often develops in people with severe heart failure, or in end of life care, it can be considered a poor sign. However, this is not always the case, and it may be found in otherwise healthy people with altitude sickness, or during sleep. In, patients with congestive heart failure and Cheyne-Stokes respiration were found to have a higher rate of mortality, especially if they experienced the breathing difficulties during their waking hours. This happens because Cheyne-Stokes respiration places further on a failing heart.
Please use one of the following formats to cite this article in your essay, paper or report: MLA Leonard, Jayne. 'What's to know about Cheyne-Stokes respiration?'
In other words, more modeling, animation, and effects tools. Paint, compositing, 3D-keying, etc. For $1000 less, you can get softimage XSI 5.0 Foundation, which provides 5-to-10 times the power of Avid 3D. Softimage xsi 7 5 keygen for mac torrent. I'd like to see some more serious functionality added to Avid 3D 3.0, myself.
Cheyne-stokes Respirations And Death Rattle
Medical News Today. MediLexicon, Intl., 6 May. APA Leonard, J. (2017, May 6). 'What's to know about Cheyne-Stokes respiration?' Medical News Today.
Retrieved from. Please note: If no author information is provided, the source is cited instead. Recommended related news.